K8 images
The K8 Helm packs would be available as a separate bundle in the package provided by distribution. However, this section can be referred to understand and generate the K8 Helm images.
Following are the steps to deploy K8 images in Mongo DB and PostgreSQL.
Mongo DB
In this deployment approach, the holdings-helm-pack-mongo-<release_number>.zip is used to load the docker images and then deploy the service in Kubernetes cluster.
Prerequisite
Following are the two prerequisites before starting the Mongo scripts.
- Mongo database scripts are executed and the database is up and running.
- Active Kafka instances that need to be configured for transact, event processor and generic ingestion (communicating with Account Aggregation) respectively.
Install a standalone DB Name DB server manually.
Alternatively, follow these steps to execute the database startup scripts (available in K8 on-premise package) to install and start the database server automatically.
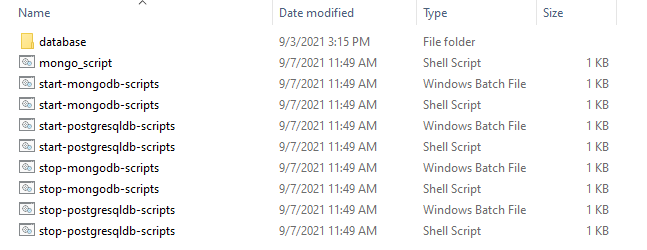
- Navigate to the folder where the database startup scripts can be found (Holdings-Docker\k8\on-premise\db).
- Execute the following database scripts.
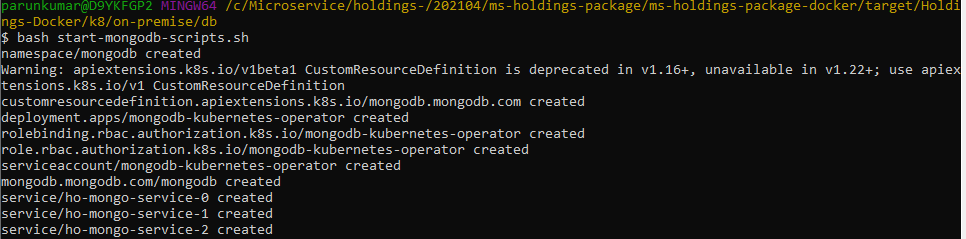
- For Windows: start-mongodb-scripts.bat
- For Linux: start-mongodb-scripts.sh
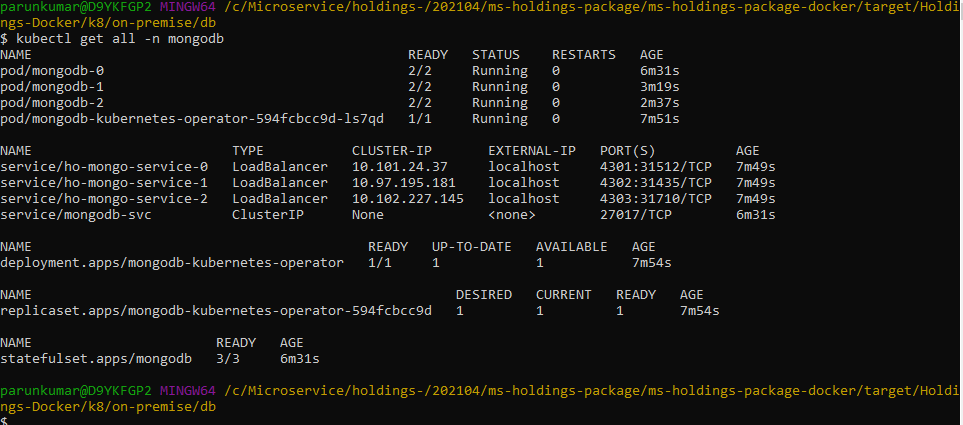
- Execute kubectl get all -n <namespace> to see all the resources for the particular database.
Deployment
Follow the below steps to start the service:
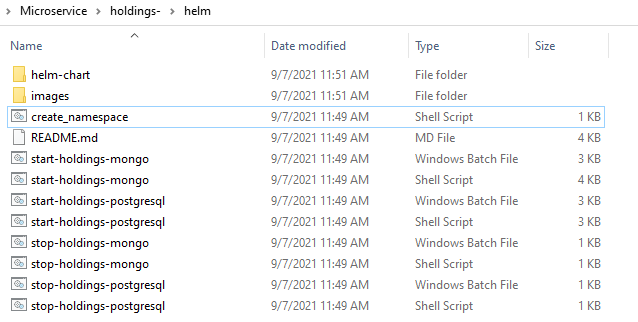
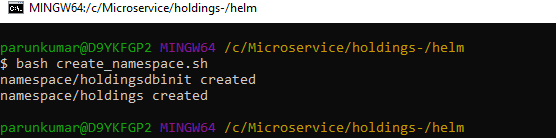
- Navigate to the extracted holdings-helm-pack-mongo-<release_number>.zip.
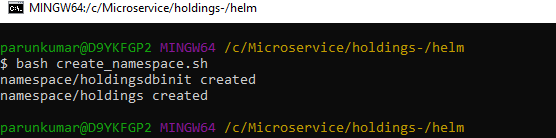
- Execute the file create_namespace.sh in Linux shell.
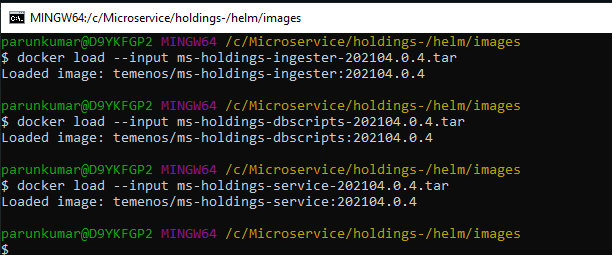
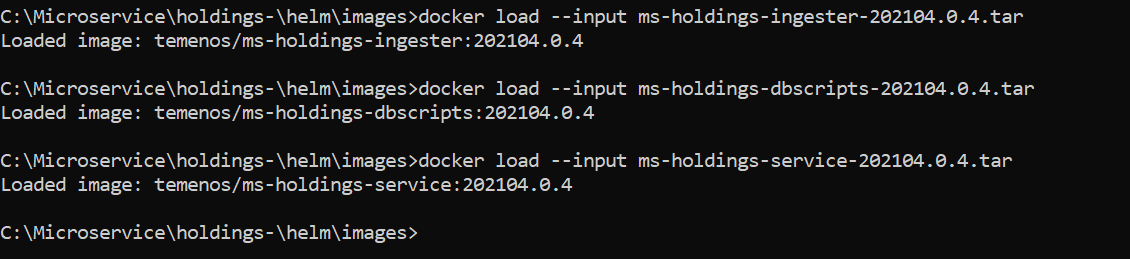
- Navigate to the images folder where the service, ingester and database images are available and load the images on the docker using the command docker load --input <image-name>.
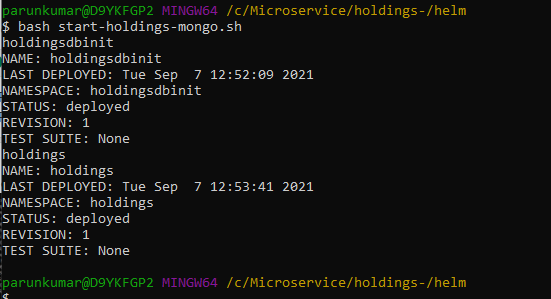
- Navigate to the folder where service startup scripts are available and open the file start-holdings-mongo.bat / start-holdings-mongo.sh.
- Configure DB and Kafka connection parameters as per the setup done as part of prerequisite step.
- Execute the respective startup script as required.
- For Windows: start-holdings-mongo.bat
- For Linux: start-holdings-mongo.sh
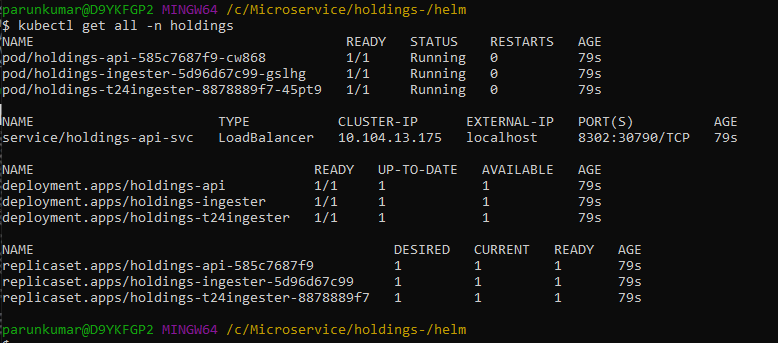
- Execute kubectl get all -n holdings to see all the resources for the particular Holdings Microservice.
Test the APIs after the successful deployment.
URL of API's follows the below structure,
Base Path: http://<DOMAIN_NAME>/<context-root>/api/<version>/
For Example: http://localhost:8304/ms-holdings-api/api/v1.0.0/
The resource path of the endpoint can be found in the swagger document.
A sample endpoint of a holdings can be http://localhost:8302/ms-holdings-api/api/v1.0.0/holdings/accounts/transactions
Undeployment
Execute the following files to stop the service.
- For Windows: stop-holdings-mongo.bat
- For Linux: stop-holdings-mongo.sh
PostgreSQL
In this deployment approach, the holdings-helm-pack-postgres-<release_number>.zip is used to load the docker images and then deploy the service in Kubernetes cluster.
Prerequisite
Following are the two prerequisites before starting the PostgreSQL scripts.
- PostgreSQL database scripts are executed and the database is up and running.
- Active Kafka instances that need to be configured for transact, event processor and generic ingestion (communicating with Account Aggregation) respectively.
Install a standalone PostgreSQL DB server manually.
Alternatively, follow these steps to execute the database startup scripts (available in K8 on-premise package) to install and start the database server automatically.
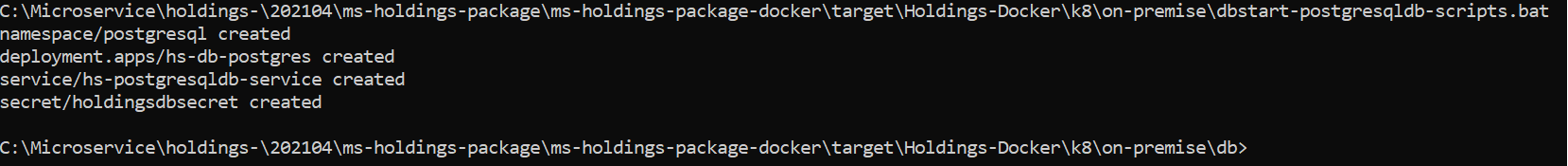
- Navigate to the folder where the database startup scripts can be found (Holdings-Docker\k8\on-premise\db).
- Execute the following database scripts.
- For Windows: start-postgresqldb-scripts.bat
- For Linux: start-postgresqldb-scripts.sh
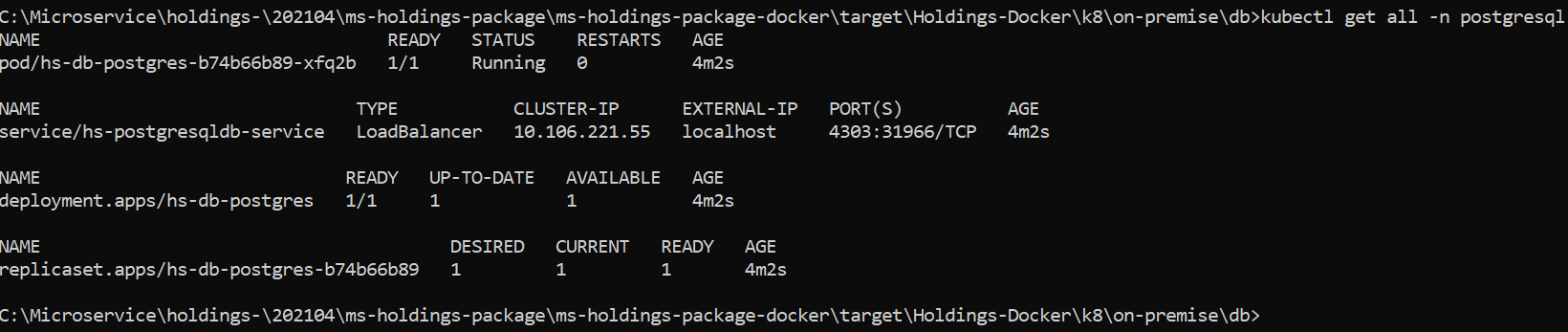
- Execute kubectl get all -n <namespace> to see all the resources for the particular database.

Deployment
Follow the below steps to start the service:
- Navigate to the extracted holdings-helm-pack-postgres-<release_number>.zip.
- Execute the file create_namespace.sh in Linux shell.
- Navigate to the images folder where the service, ingester and database images are available and load the images on the docker using the command docker load --input <image-name>.
- Navigate to the folder where service startup scripts are available and open the file start-holdings-postgresql.bat / start-holdings-postgresql.sh.
- Configure DB and Kafka connection parameters as per the setup done as part of prerequisite step.
- Execute the respective startup script as required.
- For Windows: start-holdings-postgresql.bat
- For Linux: start-holdings-postgresql.sh
- Execute kubectl get all -n holdings to see all the resources for the particular Holdings Microservice.
Test the APIs after the successful deployment.
URL of API's follows the below structure,
Base Path: http://<DOMAIN_NAME>/<context-root>/api/<version>/
For Example: http://localhost:8304/ms-holdings-api/api/v1.0.0/
The resource path of the endpoint can be found in the swagger document.
A sample endpoint of a holdings can be http://localhost:8302/ms-holdings-api/api/v1.0.0/holdings/accounts/transactions


Undeployment
Execute the following files to stop the service.
- For Windows: stop-holdings-postgresql.bat
- For Linux: stop-holdings-postgresql.sh
In this topic