Deploying Service Request Microservice on K8 (Kubernetes)
This section explains how to deploy the Service Request Microservice on K8. To do so, you need to perform the following tasks:
Deployment Artefacts
Service Request Microservices for docker deployment is available as single release bundle ms-servicerequest-package-docker-<release_number>.zip. Kubernetes (k8) pack is available inside src/docker.
Prerequisite
- Install Docker Engine in the deployment environment.
- Turn on Linux containers in docker.
Enabling Kubernetes
Follow these steps to enable kubernetes:
- After the docker is installed, enable Kubernetes in the Docker Desktop app.
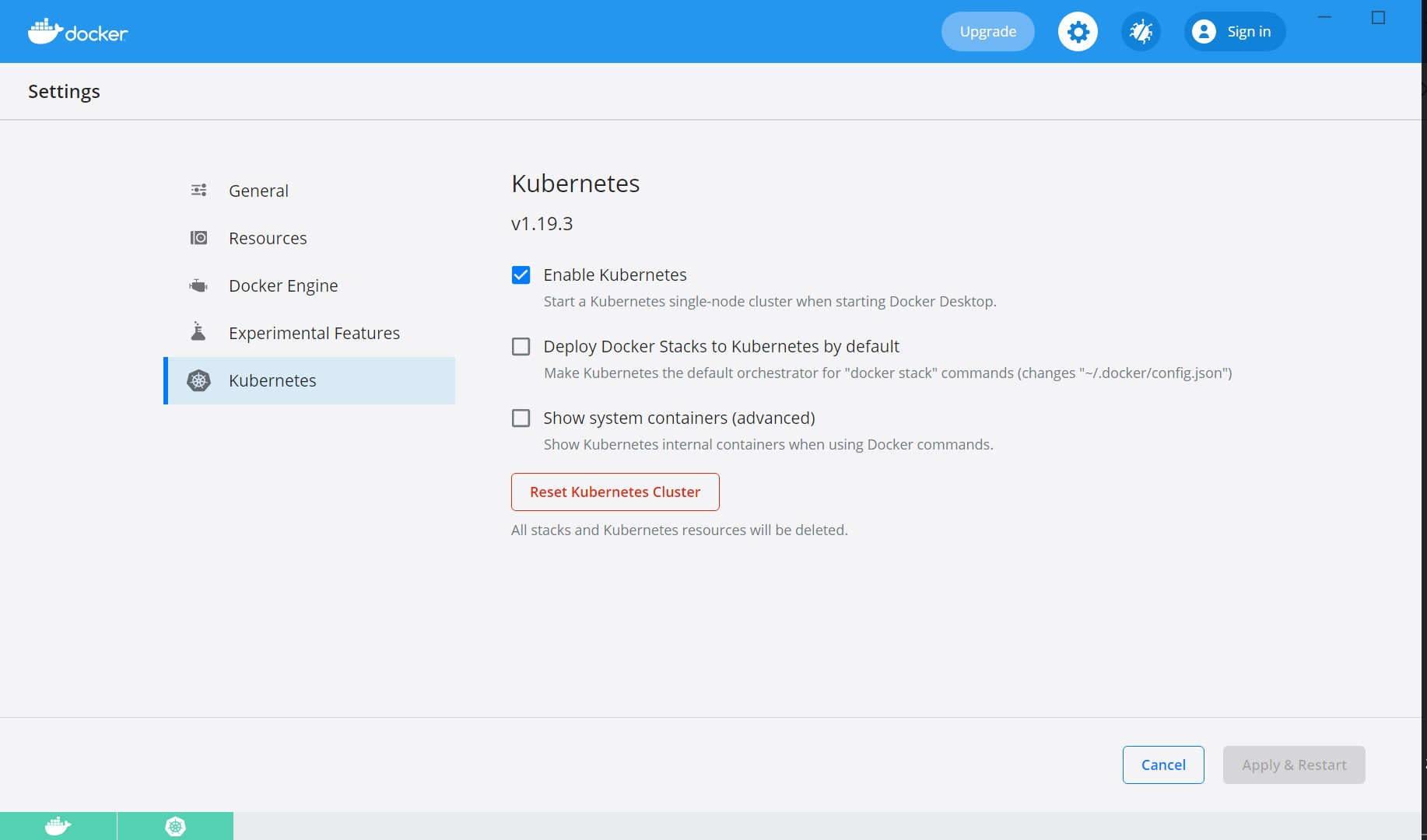
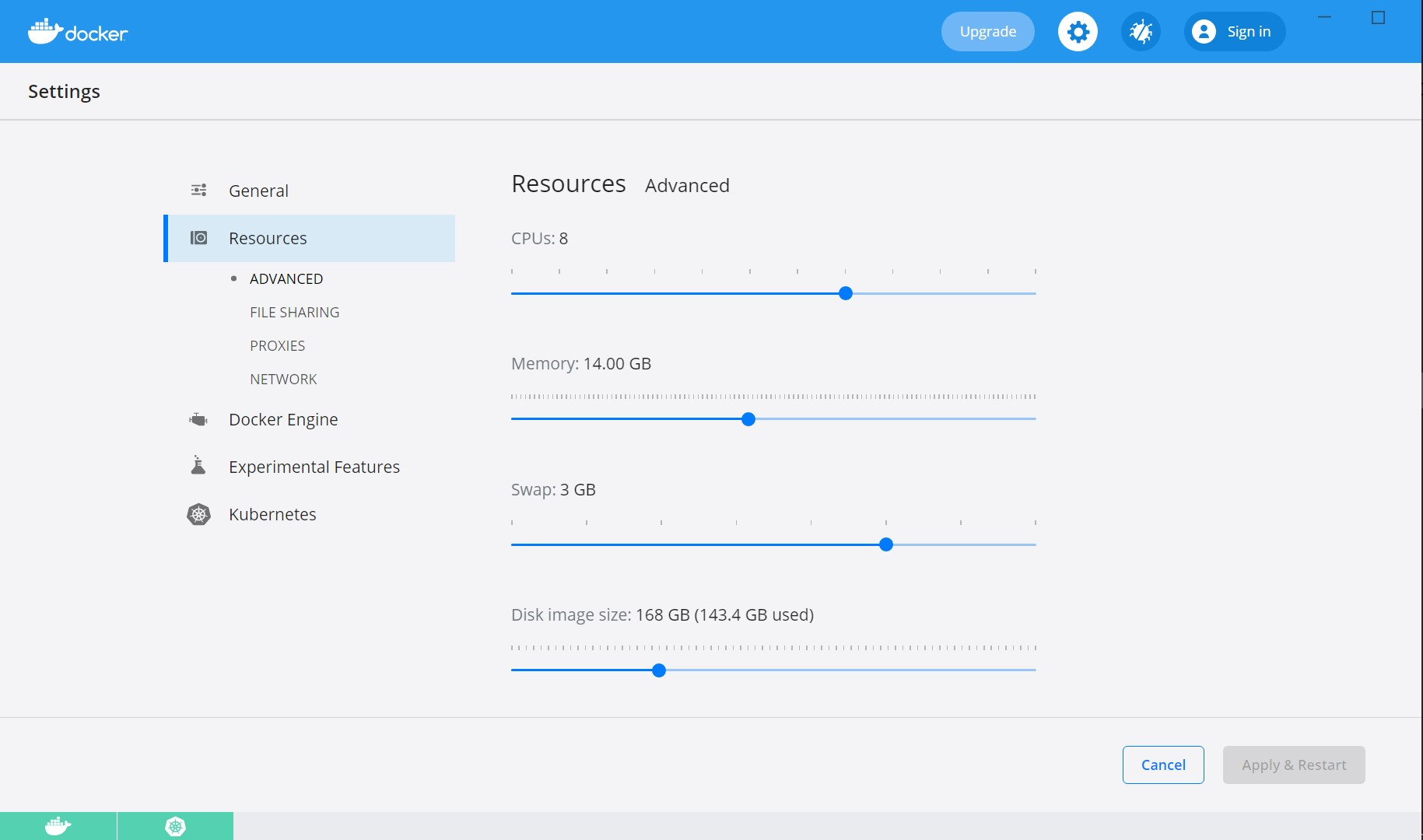
- Kubernetes requires a minimum of six CPUs to run smoothly. Go to Docker settings > Resources and increase the CPU and Memory.
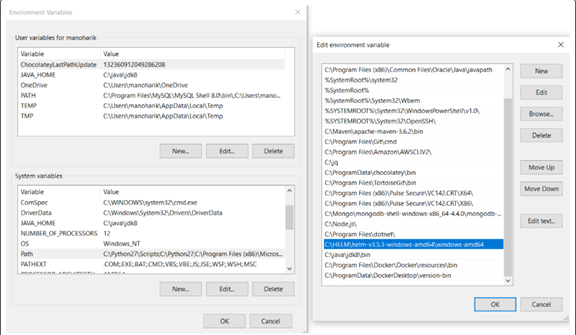
- Install Helm and set helm path as an environment variable on the system.
Enabling Strimzi for Kubernetes Cluster
If Strimzi is not installed in the machine, navigate into the streams folder and run ./strimzi-install.sh. This is a one-time step and must be repeated if we reset our Kubernetes cluster. For more information, refer to Service-Request K8 : Setting Up Kafka using Strimzi
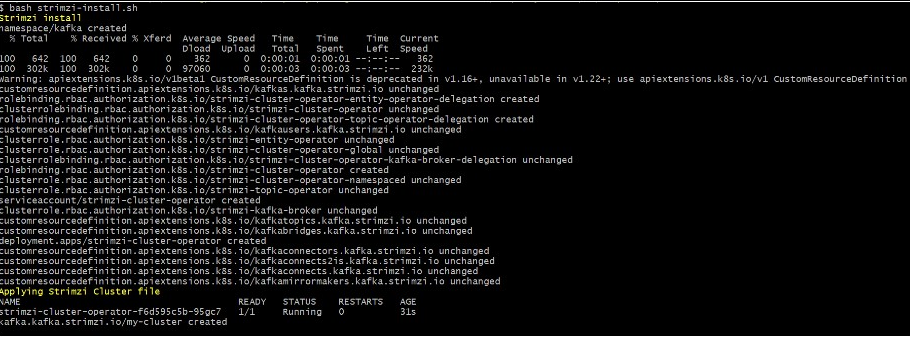
- Execute kubectl get all -n kafka in order to check all pods are up and running.
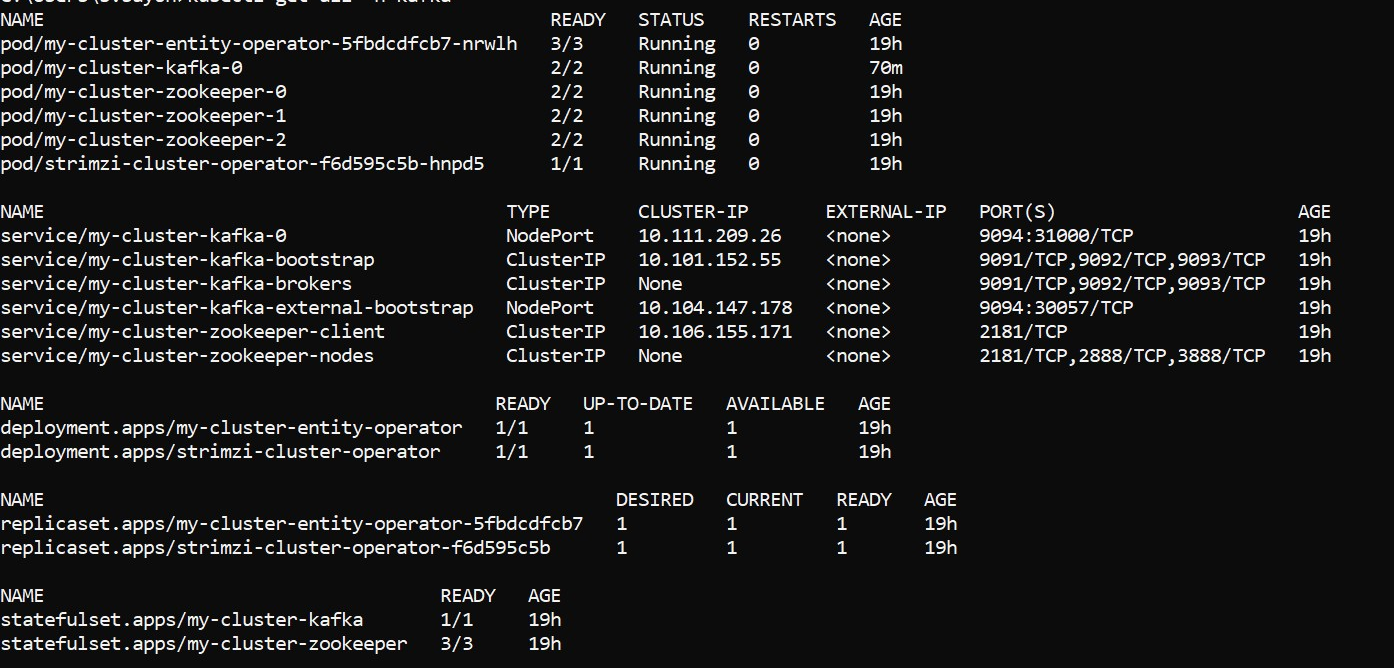
Deployment of SRMS on K8
K8 Images
The K8 Helm packs are available as a separate bundle in the package provided by distribution. However, Service-Request Helm Images Generationsection can be referred to understand on how to generate the K8 Helm images.
Mongo DB
To deploy service request on Mongo DB, follow these steps:
In this deployment approach, we use the servicerequest-helm-pack-mongo-<release_number>.zip to load the docker images and then deploy the service in kubernetes cluster and Install a standalone MongoDB server manually.
Follow these steps to start the service:
- Navigate to the extracted
servicerequest-helm-pack-mongo-<release_number>.zip file : servicerequest-helm-pack-mongo-<release_number>\servicerequest.
- Start create-namespace file by using the command bash create_namespace.sh for creating the respective namespace.
- Navigate to the images folder where the service, ingester and database images are available and load the images on the docker using the command docker load --input <image-name>.

- Once the images are loaded in to the docker, open the start-servicerequest-mongo.bat/start-servicerequest-mongo.sh by navigating to the folder where service startup scripts are available and then configure DB and Kafka connection parameters as per prerequisite step.
- Execute the following startup scripts
- For Windows : start-servicerequest-mongo.bat
- For Linux : start-servicerequest-mongo.sh
- Once the services are up and running, perform kubectl get all -n servicerequest to see all the resources for the particular Servicerequest microservice.
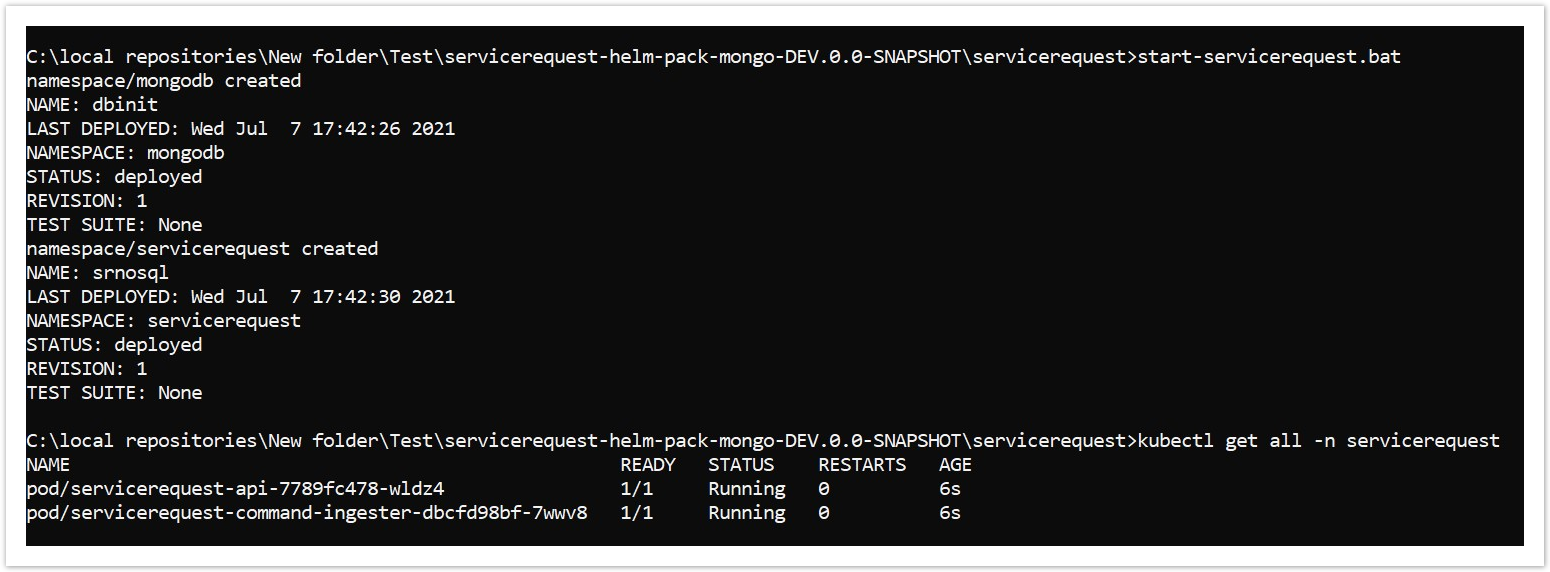
- Once the deployment is successful, the APIs can be tested.
URL of APIs follows the below structure,
- Base Path:
http://<IP_ADDRESS>:<PORT>/<context-root>/api/<version>/ For Example: http://localhost:8310/ms-servicerequest-api/api/v1.0.0/ - The resource path of the endpoint can be found in the swagger document.
- A sample endpoint of a service request can be
http://localhost:8310/ms-servicerequest-api/api/v1.0.0/reference?type=Type
- Base Path:
Undeployment
Execute the files to stop the service.
- For Windows : stop-servicerequest-mongo.bat
- For Linux : stop-servicerequest-mongo.sh
PostgreSQL
To deploy service request on PostgreSQL, follow these steps:
In this deployment approach, we use the servicerequest-helm-pack-postgres-<release_number>.zip to load the docker images and then deploy the service in kubernetes cluster and Install a standalone PostgreSQL DB server manually.
Follow these steps to start the service:
- Navigate to the extracted
servicerequest-helm-pack-postgres-<release_number>.zip file : servicerequest-helm-pack-mongo-<release_number>\servicerequest.
- Start create-namespace file by using the command bash create_namespace.sh for creating the respective namespace.
- Navigate to the images folder where the service, ingester and database images are available and load the images on the docker using the command docker load --input <image-name>.

- Once the images are loaded in to the docker, open the start-servicerequest-postgresql.bat/start-servicerequest-postgresql.sh by navigating to the folder where service startup scripts are available and then configure DB and Kafka connection parameters as per prerequisite step.
- Execute the following database scripts
- For Windows : start-servicerequest-postgresql.bat
- For Linux : start-servicerequest-postgresql.sh
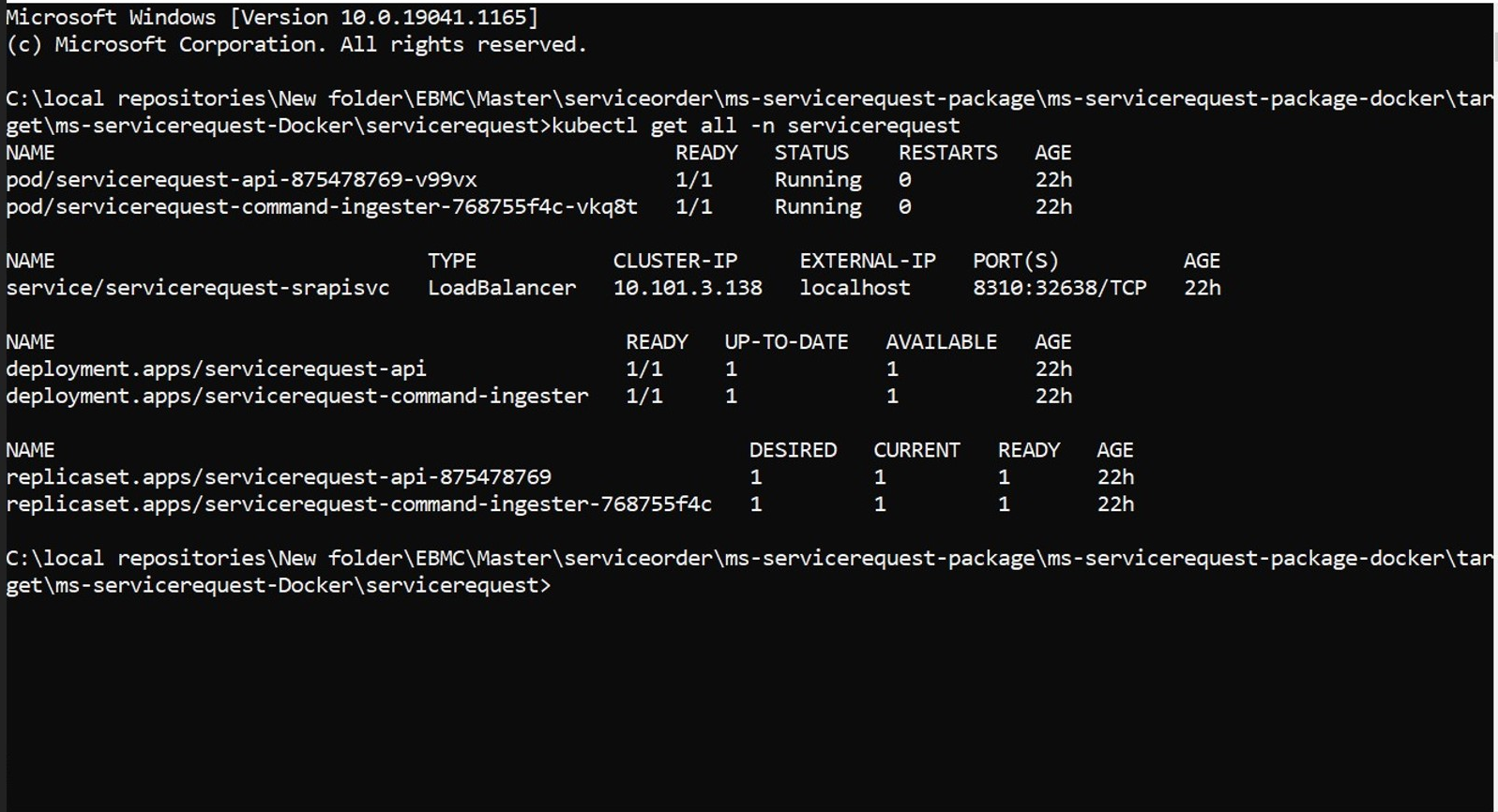
- Once the database are up and running, perform kubectl get all -n servicerequest to see all the resources for the particular Servicerequest microservice.
- Once the deployment is successful, the APIs can be tested.
- Base Path:
http://<IP_ADDRESS>:<PORT>/<context-root>/api/<version>/ For Example: http://localhost:8310/ms-servicerequest-api/api/v1.0.0/ - The resource path of the endpoint can be found in the swagger document.
- A sample endpoint of a service request can be
http://localhost:8310/ms-servicerequest-api/api/v1.0.0/reference?type=Type
URL of APIs follows the below structure,
Undeployment
Execute the files to stop the service.
- For Windows : stop-servicerequest-postgresql.bat
- For Linux : stop-servicerequest-postgresql.sh
K8 Ingress
K8 Ingress deployment approach exposes the Service Request MS APIs through the domain name "servicerequest.com" and is implemented based on the nginx ingress controller in K8 pack.
Follow the steps below (prior to deployment of the K8 packs) to configure and access the MS APIs through the domain name.
URL of APIs follows the below structure,
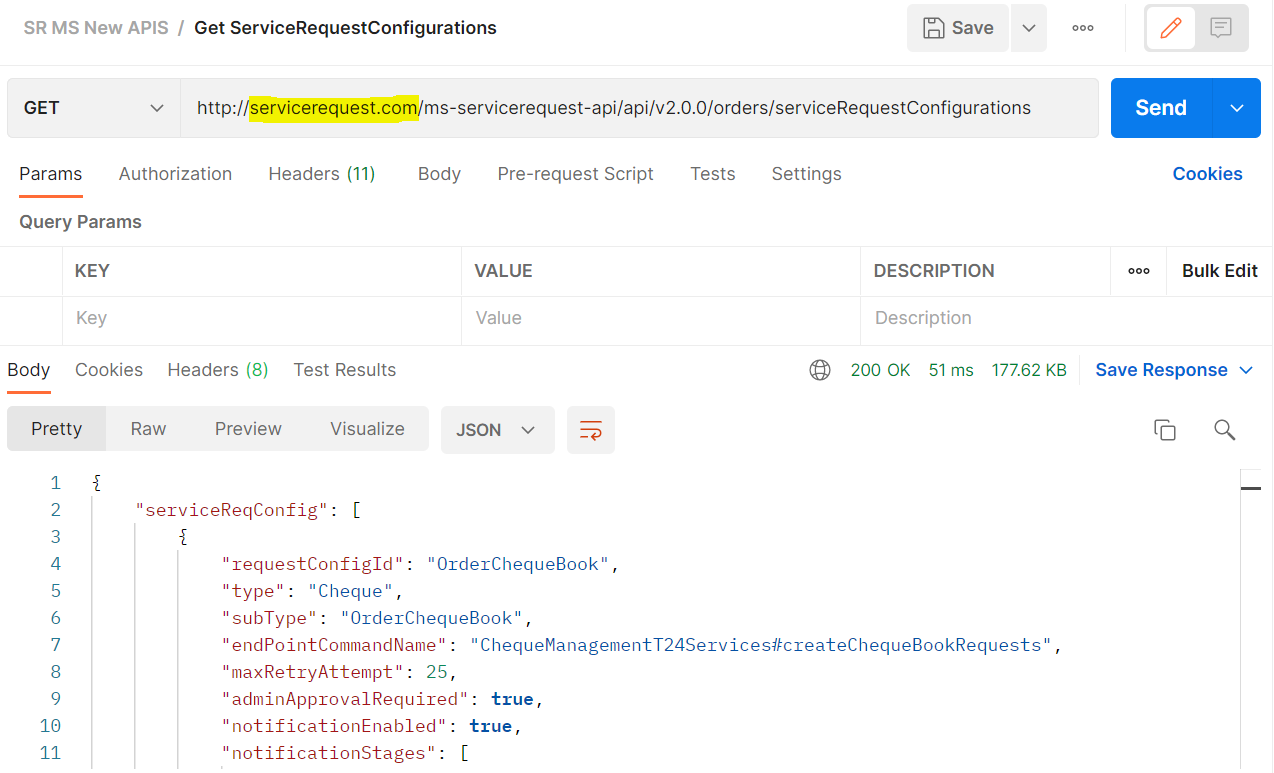
- Base Path: http://<DOMAIN_NAME>/<context-root>/api/<version>/. For Example: http://servicerequest.com/ms-servicerequest-api/api/v2.0.0/.
- The resource path of the endpoint can be found in the swagger document.
- Before the deployment of the K8 packs, configure and access the MS APIs through the domain name.
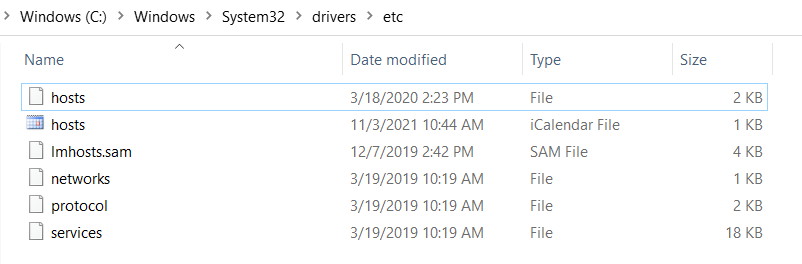
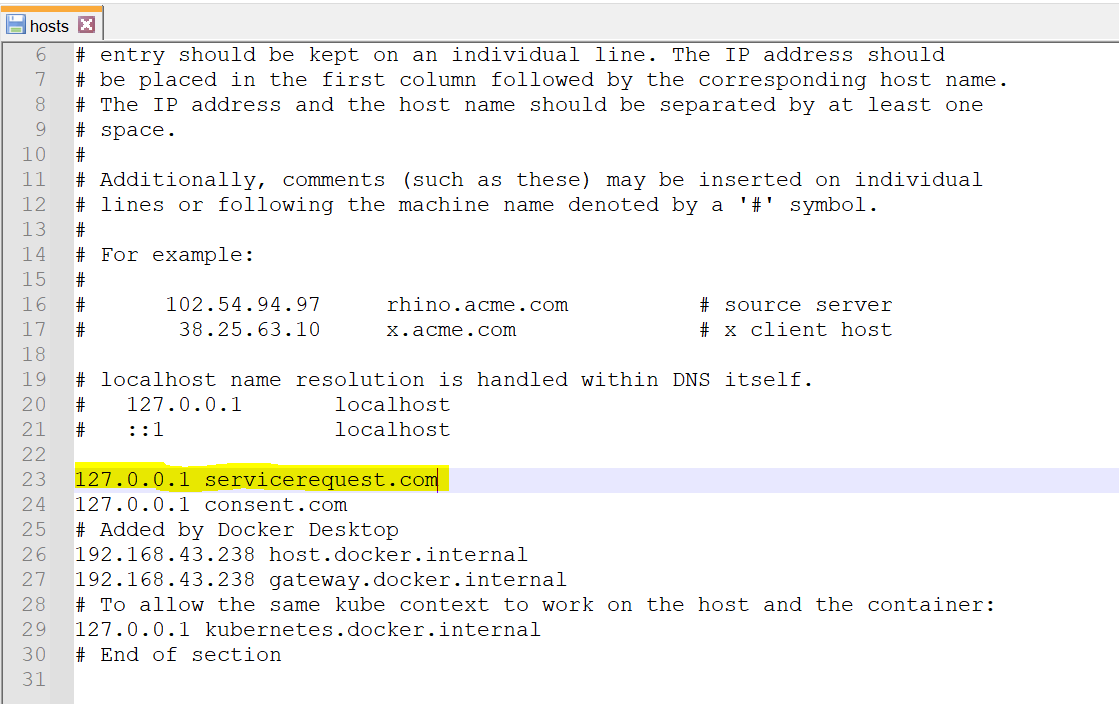
- Navigate to C:\Windows\System32\drivers\etc and set the domain name ("127.0.0.1 servicerequest.com") in the hosts file of Windows and then restart the machine/server to reflect the changes.
- Install K8 (Helm images) packs package from the samples/operator folder and execute start-ingress-controller.bat/start-ingress-controller.sh file to start the ingress controller and then deploy the K8 (Helm images) packs by following the respective deployment instructions.
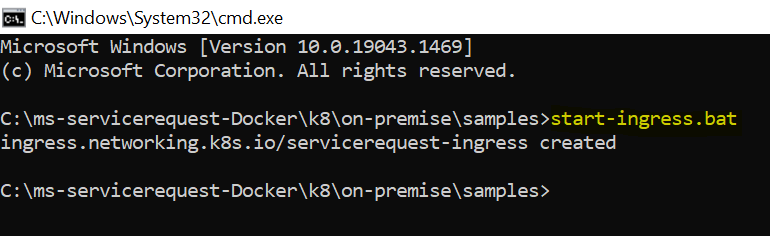
- Navigate to K8 (Helm images) package from the samples folder and execute start-ingress.bat/start-ingress.sh to start the ingress services
- Access the ServiceRequest APIs using the domain name (servicerequest.com).
Undeployment
To undeploy the ingress, navigate to K8 (Helm images) package and then execute the stop-ingress.bat/stop-ingress.sh to stop the service.
Helm Images Generation
The K8 Helm packs are available as a separate bundle in the package provided by distribution. Follow the below steps to generate the K8 helm pack:
Mongo DB
In this deployment approach, use the servicerequest-helm-pack-mongo-<release_number>.zip to load the docker images for MongoDB and then follow the below steps to generate the helm images for API, DB initialization from the Docker package
- Navigate to serviceorder\ms-servicerequest-package\ms-servicerequest-package-docker\src\docker folder path.
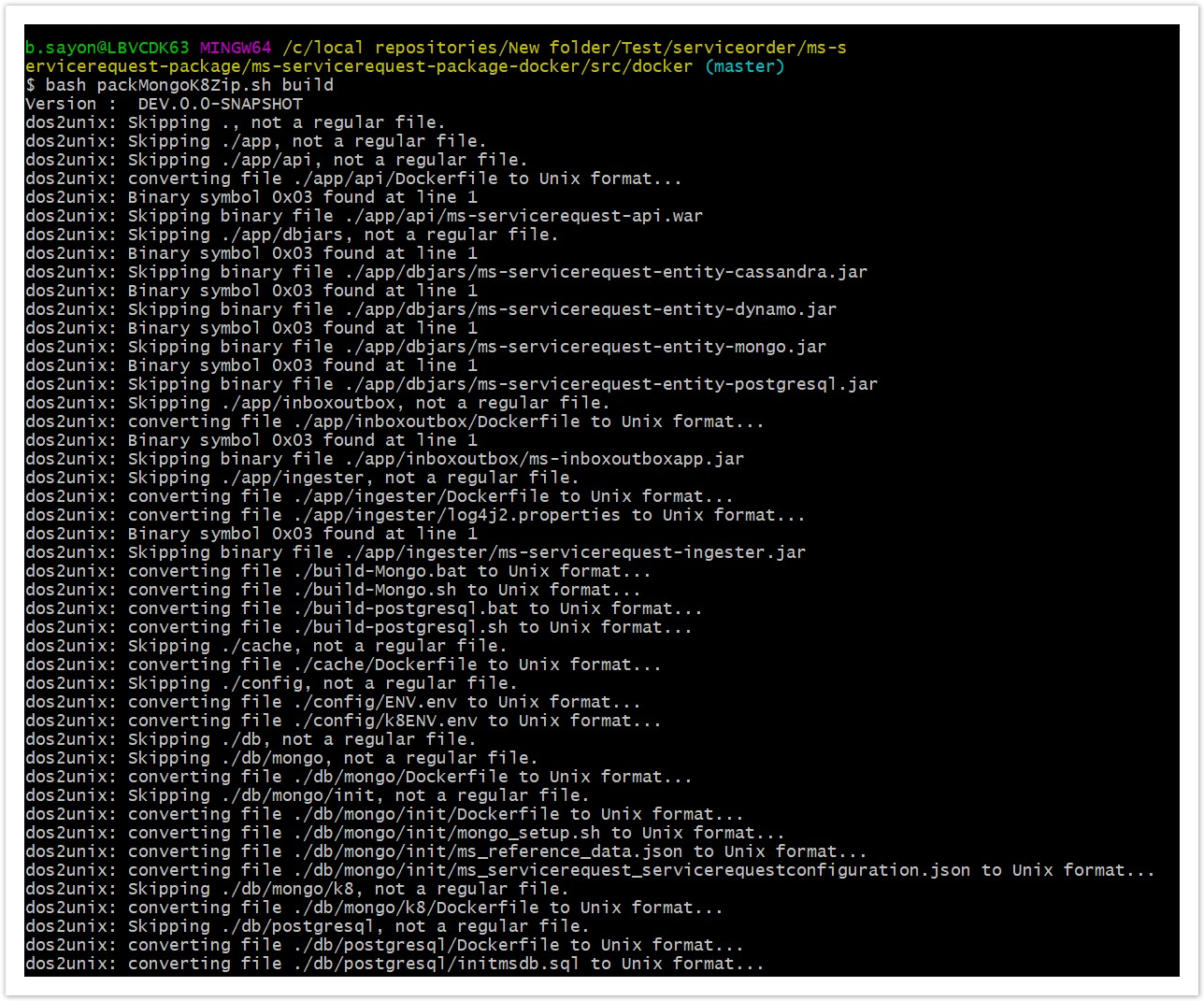
- Start the packMongoK8Zip.sh file which in turns builds the docker images and generates the servicerequest-helm-pack-mongo-<release_number>.zip file
- Use command: bash packMongoK8Zip.sh build in linux shell to execute the file.
- Navigate to serviceorder\ms-servicerequest-package\ms-servicerequest-package-docker and execute the command mvn -f mongo-helm-pack.xml install to generate the servicerequest-helm-pack-mongo-<release_number>.zip.
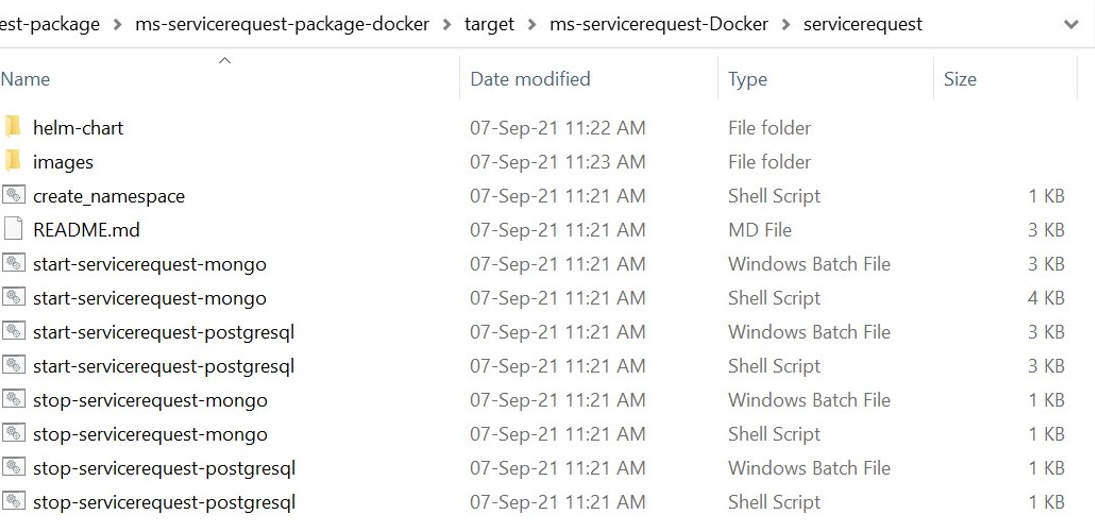
- After the build is completed, navigate to serviceorder\ms-servicerequest-package\ms-servicerequest-package-docker\target. The servicerequest-helm-pack-mongo-<release_number>.zip will be available.
- Unzip the file, it will contain the images, start-servicerequest-mongo and stop-servicerequest-mongo scripts.
PostgreSQL
In this deployment approach, use the servicerequest-helm-pack-postgres-<release_number>.zip to load the docker images for PostgreSQL DB and then follow the below steps to generate the helm images for API, DB initialization from the Docker package
- Navigate to serviceorder\ms-servicerequest-package\ms-servicerequest-package-docker\src\docker folder path.
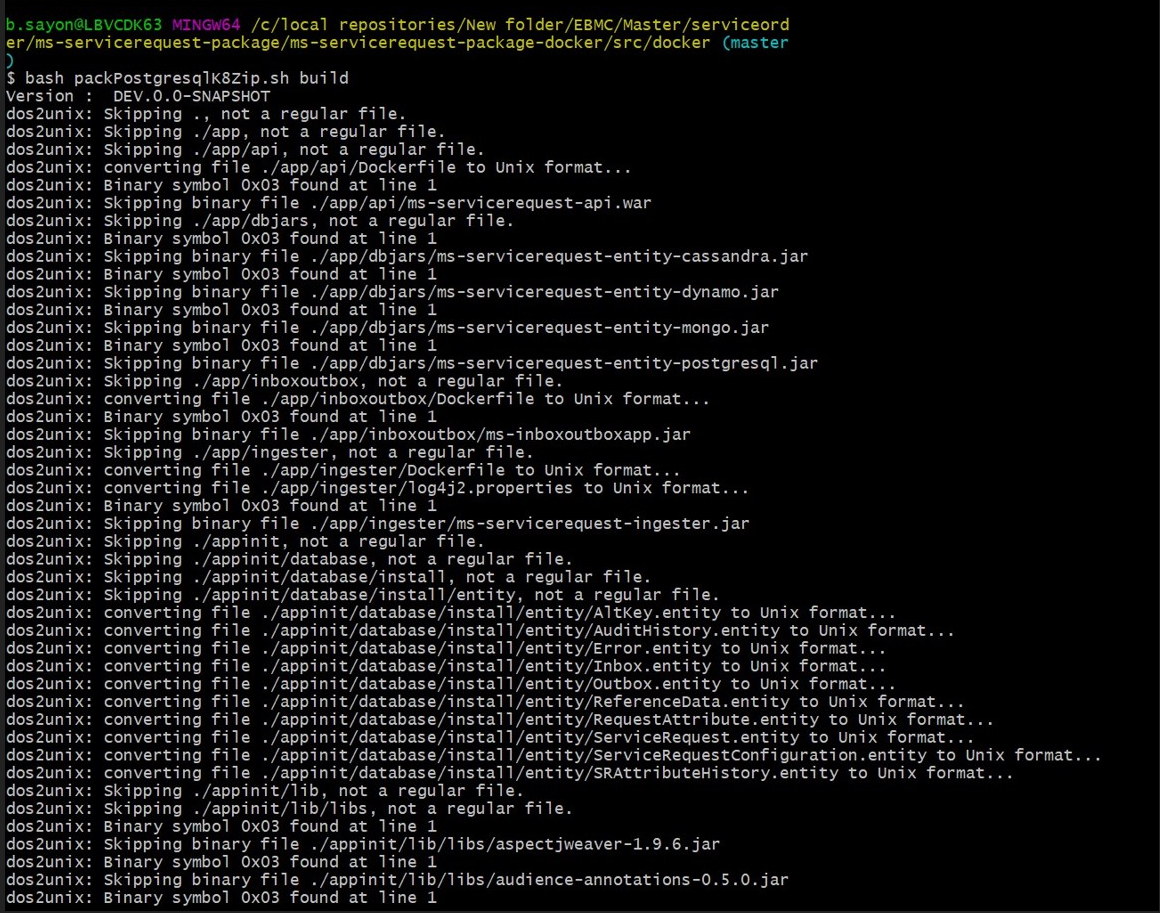
- Start the packPostgresqlK8Zip.sh file which in turns builds the docker images and generates the servicerequest-helm-pack-mongo-<release_number>.zip file.
- Use command: packPostgresqlK8Zip.sh build build in linux shell to execute the file.
- Navigate to serviceorder\ms-servicerequest-package\ms-servicerequest-package-docker and execute the command mvn -f postgres-helm-pack.xml install to generate the servicerequest-helm-pack-postgres-<release_number>.zip.
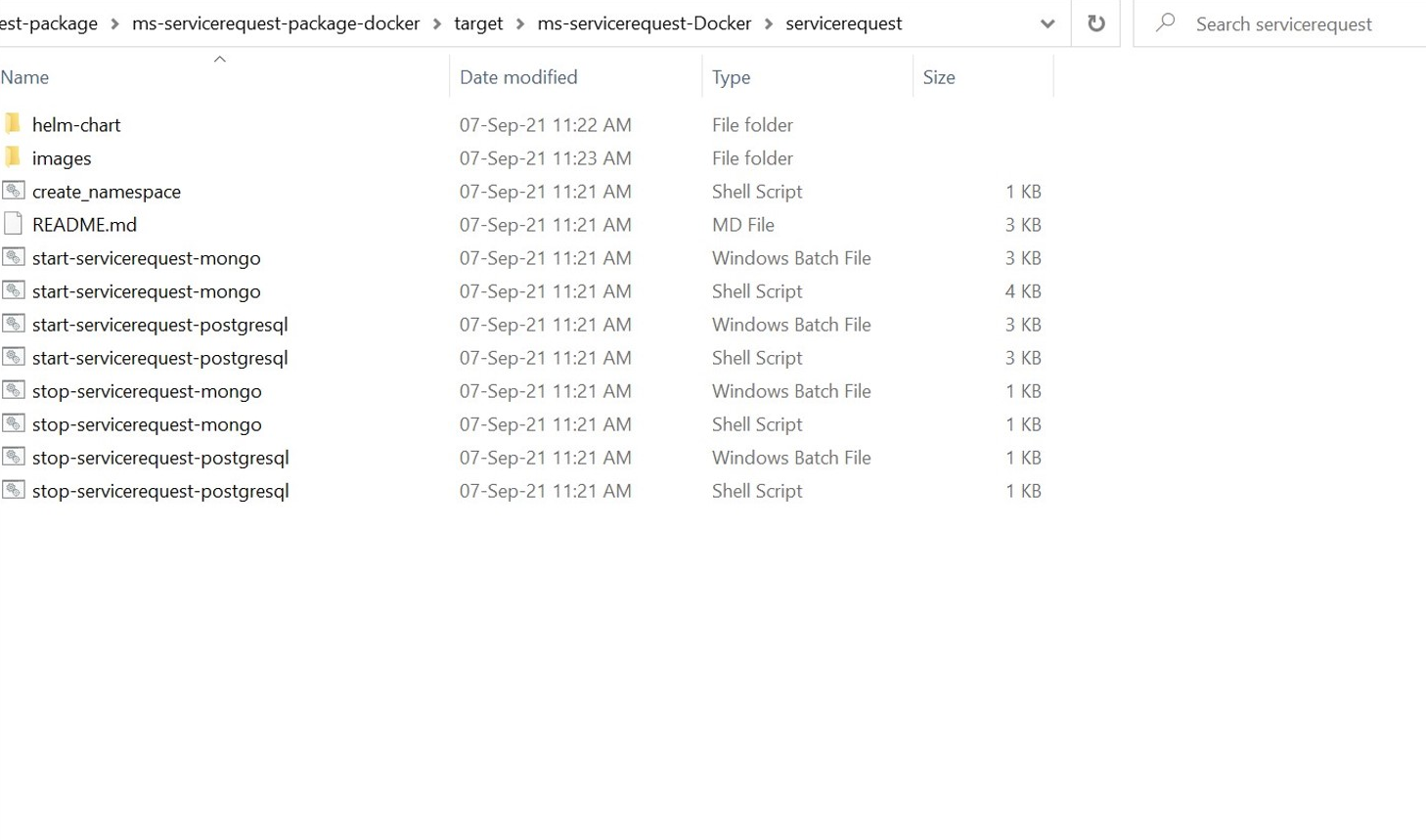
- After the build is completed, navigate to serviceorder\ms-servicerequest-package\ms-servicerequest-package-docker\target. The servicerequest-helm-pack-postgres-<release_number>.zip will be available.
- Unzip the file, it will contain the images, start-servicerequest-postgresql and stop-servicerequest-postgresql scripts.

Helm Deployment Upgrade
The helm upgrade command is used to set the new configuration changes in the existing helm chart.
Command:
helm upgrade <release-name> ./<path> -n <namespace> --set <env-variables>
Example: helm upgrade srms./svc -n servicerequest --set env.name=%ENV_NAME%
Follow the below steps to update the configuration during the runtime without the downtime.
- To upgrade an existing helm chart, navigate (ms-servicerequest-package\ms-servicerequest-package-docker\target\ms-servicerequest-helm-postgres-pack-DEV.0.0-SNAPSHOT\upgrade) to the upgrade folder in the root helm package.
- Select the batch and the shell scripts containing the upgrade commands to release a new version.
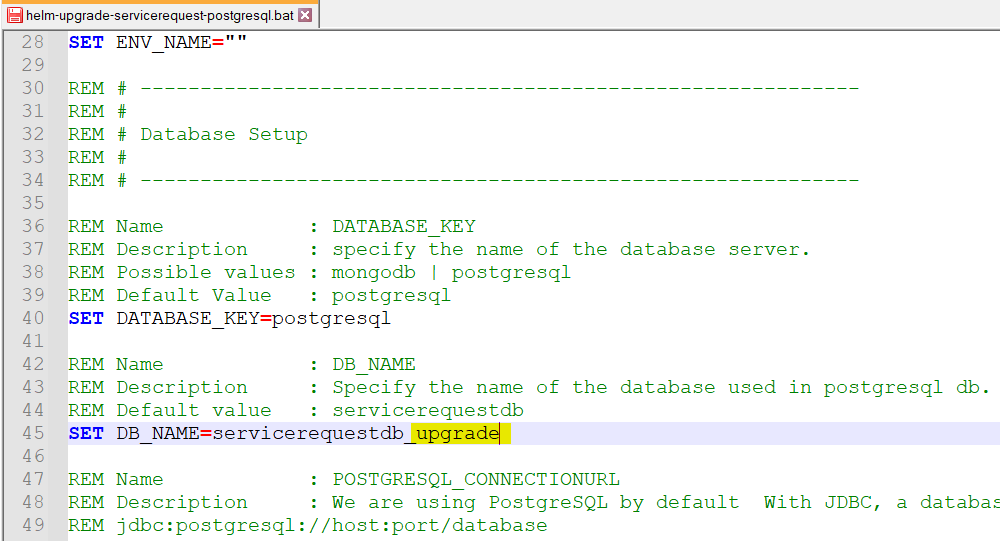
- Make the necessary changes in the helm upgrade script and save it. For example, the db_name can be updated.
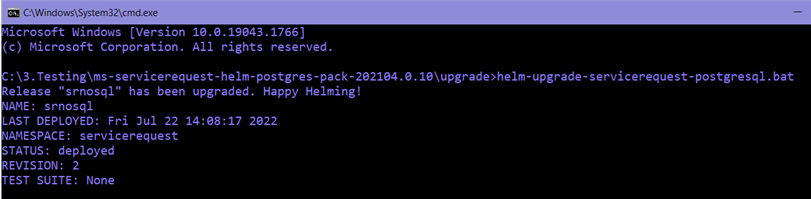
- Execute the helm-upgrade script for the deployment to be updated with the new configuration change with zero downtime.
In this topic